
What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)?
Automatic address assignment via the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol proceeds in four consecutive steps:. To begin, send the client a DHCPDISCOVER package with the target address 255.255.255.255 and the source address 0.0.0.0. With this so-called broadcast, all network users are contacted to locate available DHCP servers and inform them of the address request.
What is DHCP? How does it work? Digital Citizen
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a standard protocol defined by RFC 1541 (which is superseded by RFC 2131) that allows a server to dynamically distribute IP addressing and configuration information to clients. Normally the DHCP server provides the client with at least this basic information: IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
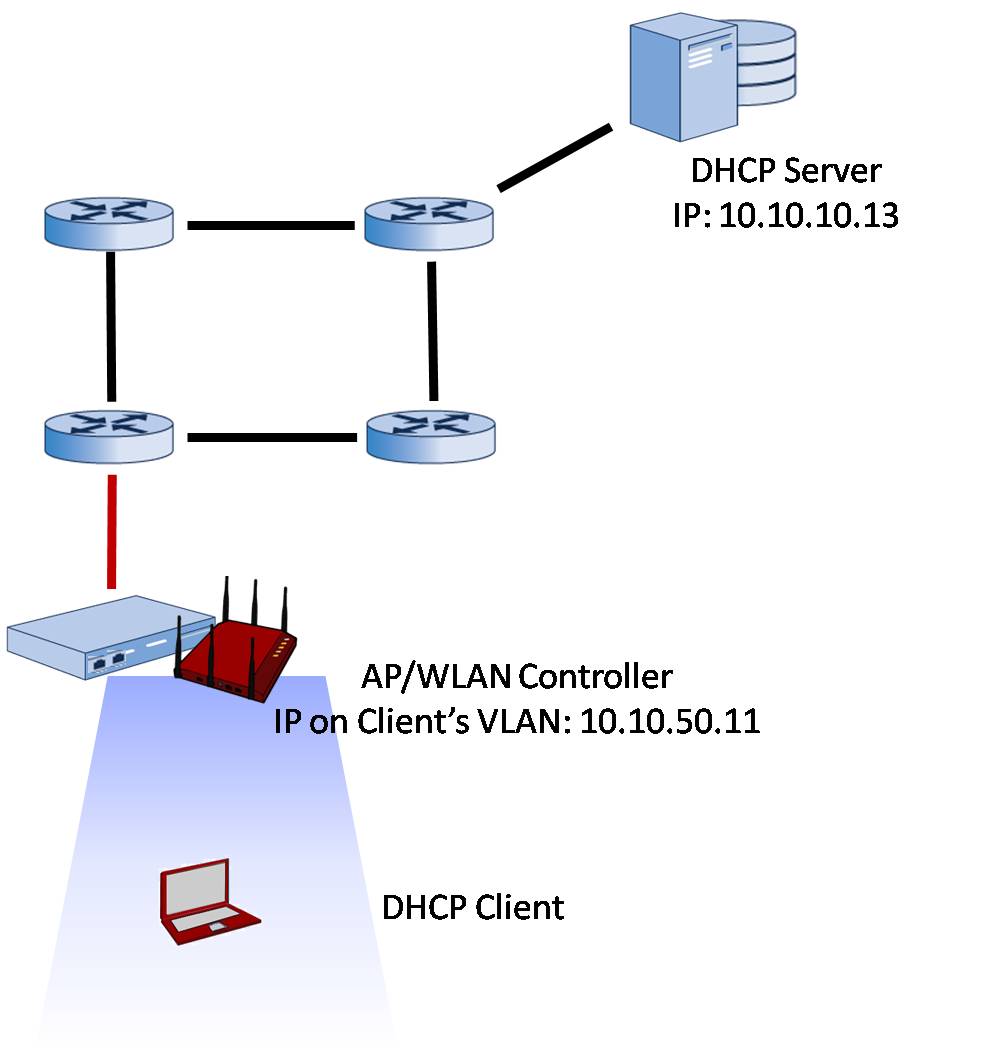
DHCP for Wireless LAN Clients
A DHCP server contains several pre-configured IP configurations. When it receives a DHCP request from a DHCP client, it provides an IP configuration to the client from all available IP configurations. This process goes through four steps: Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgment. The following image shows all four steps of a DHCP communication.

DHCP server Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol CCNA Cisco
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP is an IP network protocol that relies on client-server architecture to automatically set IP addresses and other attributes to an IP host to enable information transfer between network nodes. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol used by devices linked to the internet to guide the.
DHCP Server on Cisco Router Configure and Troubleshoot
DHCP Server: DHCP Server is basically a server that holds IP Addresses and other information related to configuration. DHCP Client: It is basically a device that receives configuration information from the server. It can be a mobile, laptop, computer, or any other electronic device that requires a connection.

DHCP Protocol Everything you need to know including working & Security
A modem connects your home network to the Internet, and a router ensures the traffic from the Internet reache the correct device on your network. Routers provide protection against attacks from the outside, and advanced administrative functions. Network switches functionally allow you to expand the number of Ethernet ports on your router.
Deployment of DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client-server architecture.. The technology eliminates the need for individually configuring network devices manually, and consists of two network.
Dhcp Server Network Diagram Dhcp, the dynamic host configuration
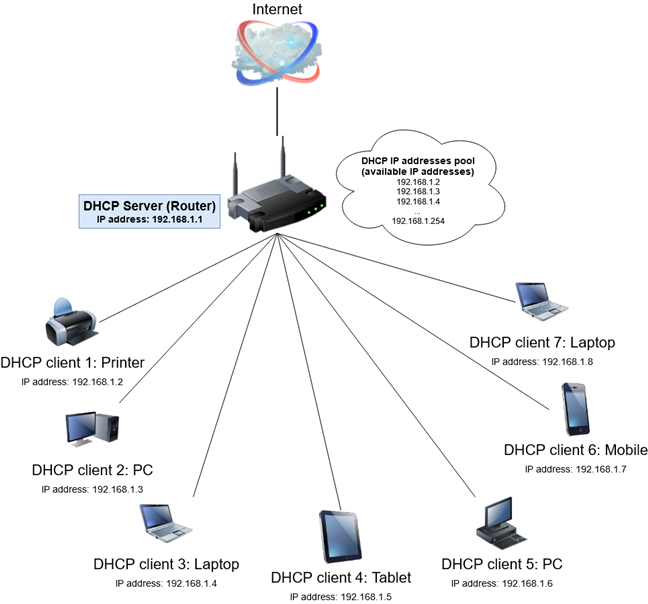
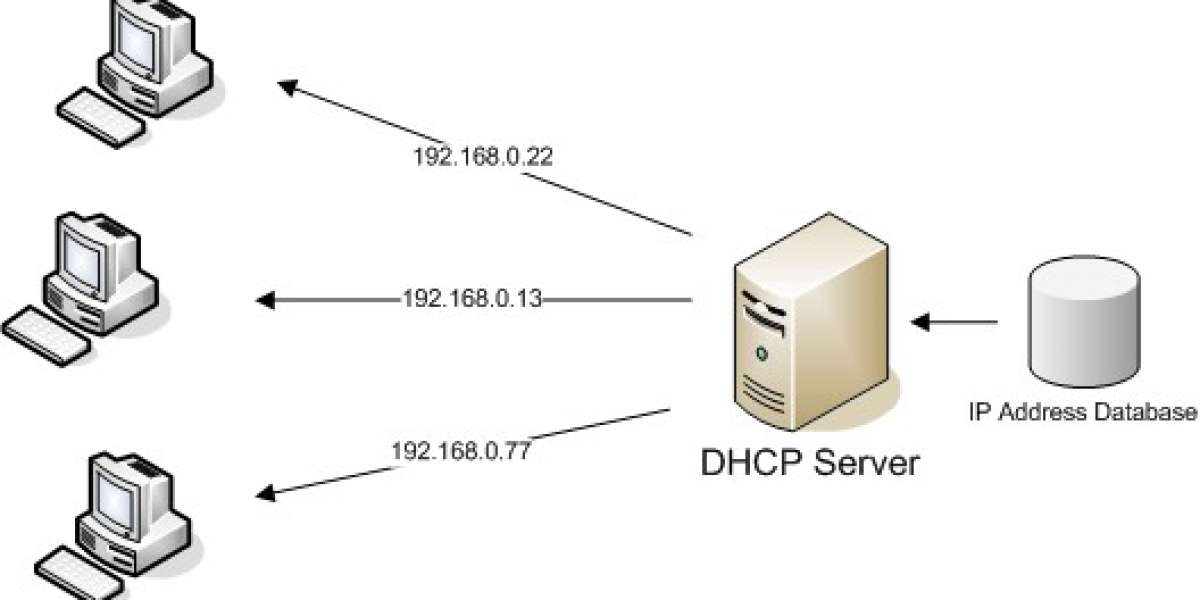
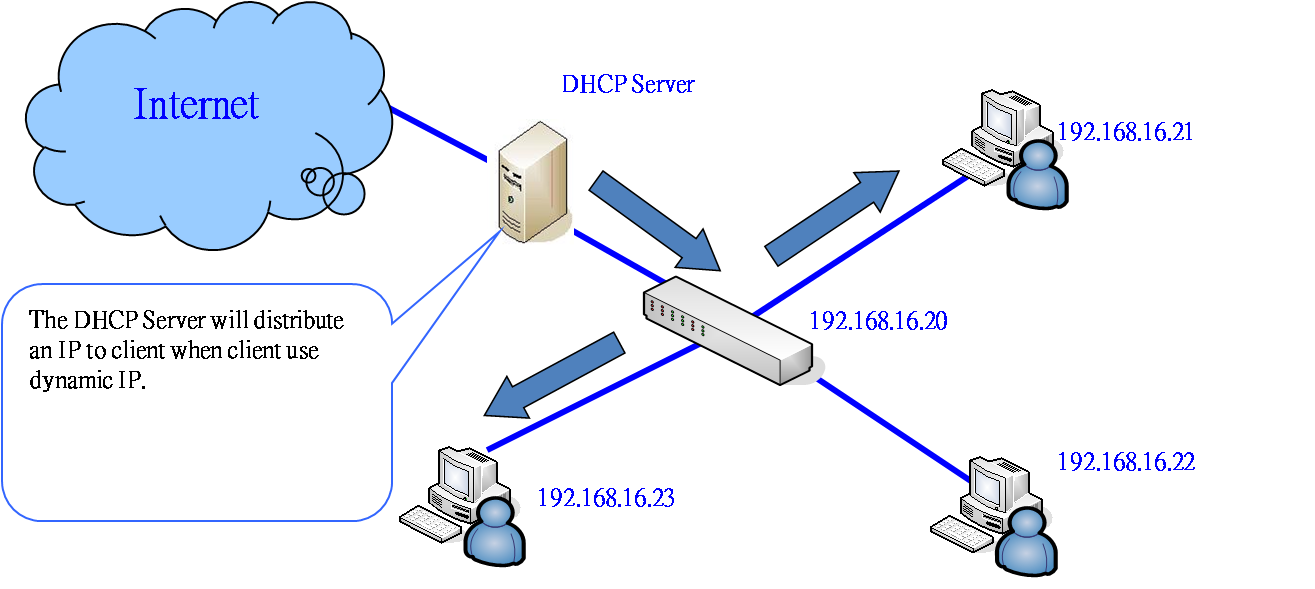
A DHCP Server is a network server that automatically provides and assigns IP addresses, default gateways and other network parameters to client devices. It relies on the standard protocol known as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP to respond to broadcast queries by clients.

How DHCP Server Assigns IP Addresses to the Client Computers? Networking
DHCP Server. A DHCP server is what the system uses to automatically provide IP addresses and additional network parameters to the devices that connect to your network. It is able to provide temporary or dynamic IP addresses taken from a pool of available addresses. In addition, a DHCP server gives permanent IP addresses and DHCP configuration.

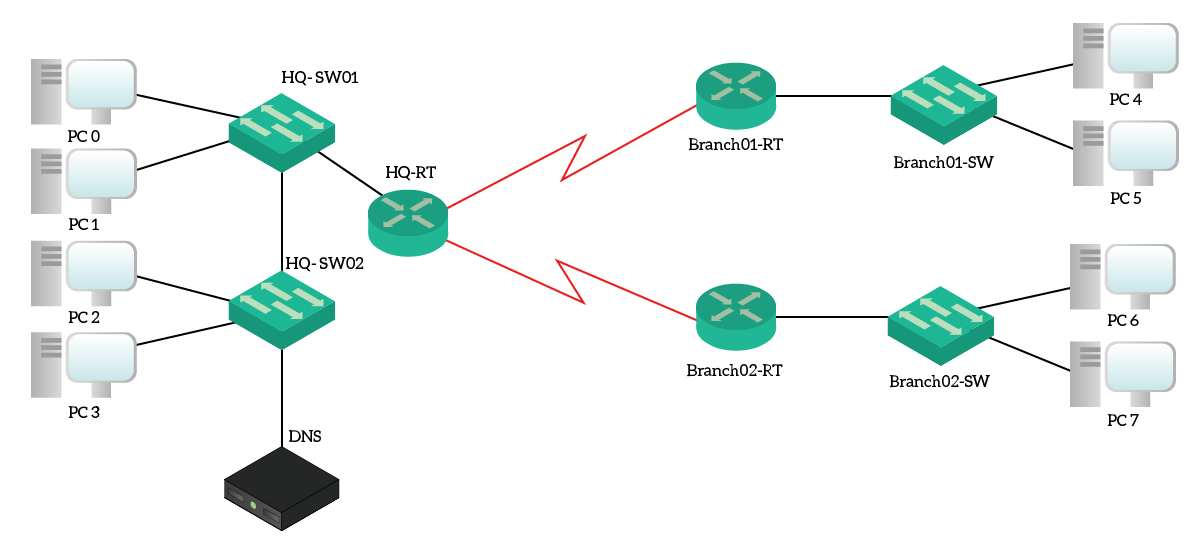
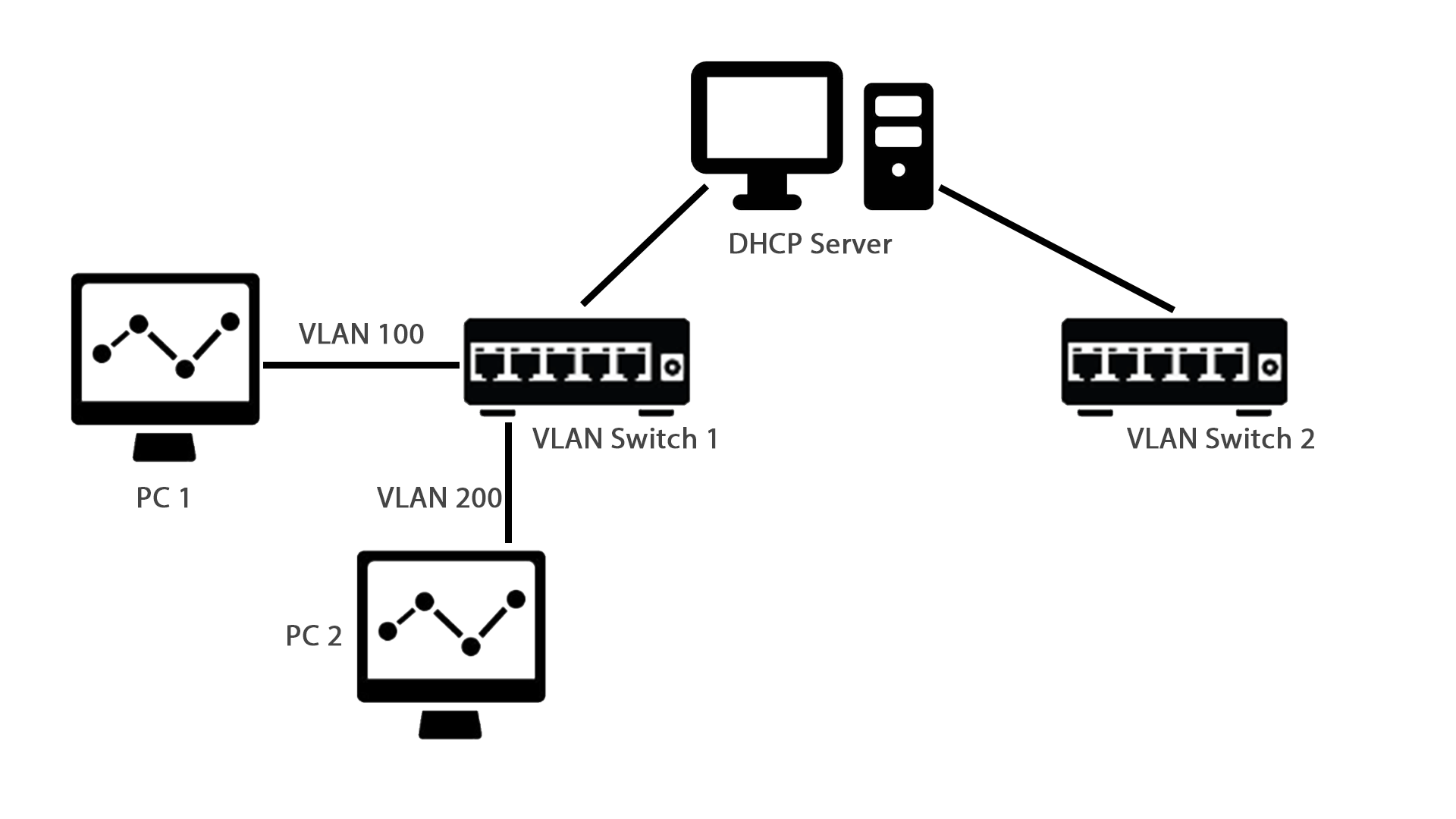
Lab DHCP Server with a VLSM network
Lab 6 Network Diagram (Note: Subnet labels and dashed borders are for informational use only) Implementation.. ip dhcp-server network add address=10.0.1.0/24 dns-server=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4 gateway=10.0.1.254 ip dhcp-server network print. After configuring clients (see below), you can check on the router to see which IP addresses have been.

4.3 Explain the role of DHCP and DNS within the network Nextgenccnas
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol that provides quick, automatic, and central management for the distribution of IP addresses within a network. It's also used to configure the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information on the device.

DHCP DNS and Web Server configuration in cisco packet tracer dhcp
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used in networks to dynamically assign IP addresses & other network configuration information like default gateway, mask, DNS server address etc. DHCP server automatically assigns IP address to various devices in network. This in turn reduces work of Network Administrator to manually assign IP address to various devices.

Dhcp Server Network Diagram Learn Diagram Images
RFC 2131 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol March 1997 3. The Client-Server Protocol DHCP uses the BOOTP message format defined in RFC 951 and given in table 1 and figure 1. The 'op' field of each DHCP message sent from a client to a server contains BOOTREQUEST. BOOTREPLY is used in the 'op' field of each DHCP message sent from a server to a.
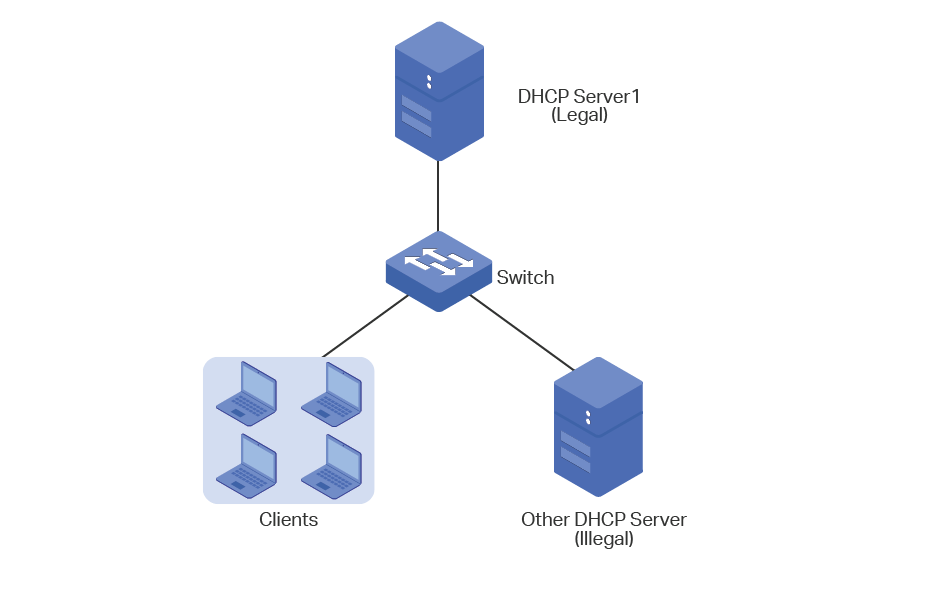
How to Configure DHCP for Multiple VLANs? sophie92578’s blog
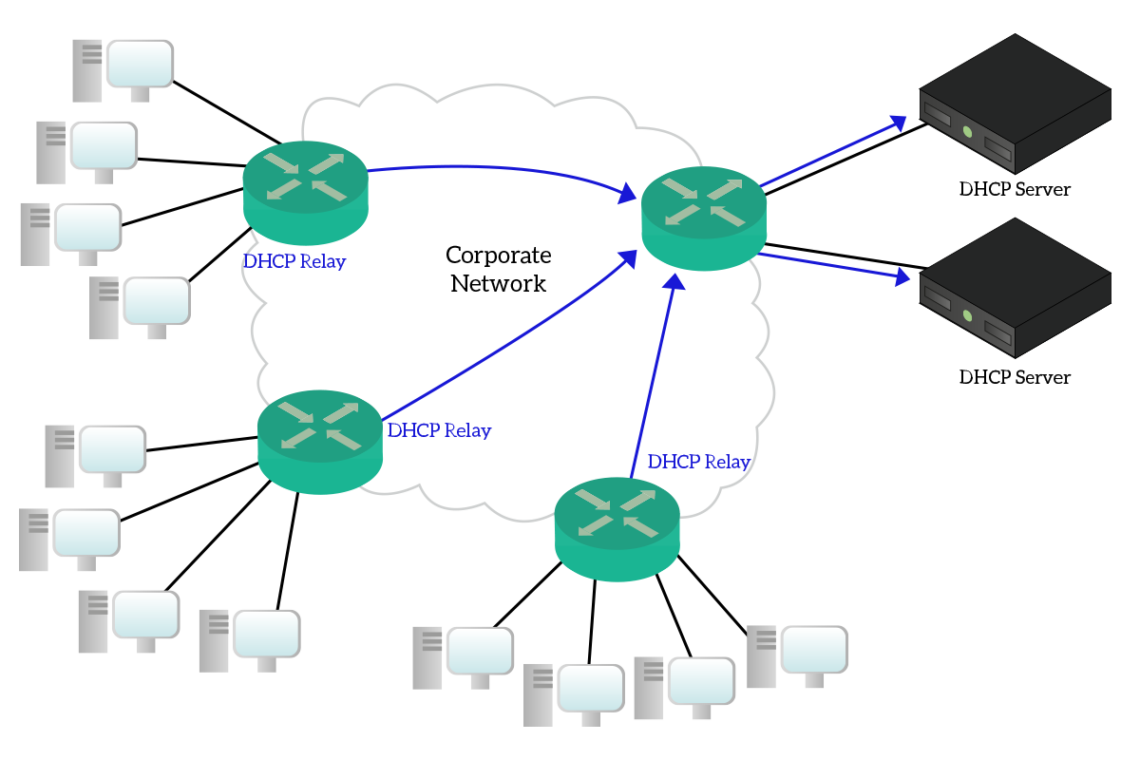
The preceding diagram shows the following steps: The client discovers a DHCP server by broadcasting a discover message to the limited broadcast address ( 255.255.255.255) on the local subnet. If a router is present and configured to behave as a BOOTP relay agent, the request is passed to other DHCP servers on different subnets.
Pengertian DHCP dan Fungsinya Lengkap Belajar Komputer Panduan
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a client/server protocol that automatically provides an Internet Protocol (IP) host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway. In DHCP, port number 67 is used for the server and 68 is used for the client.
Protocols for the network DNS, DHCP, Dynamic Routing
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol used to dynamically assign IP addresses and other network settings to devices on a local network.